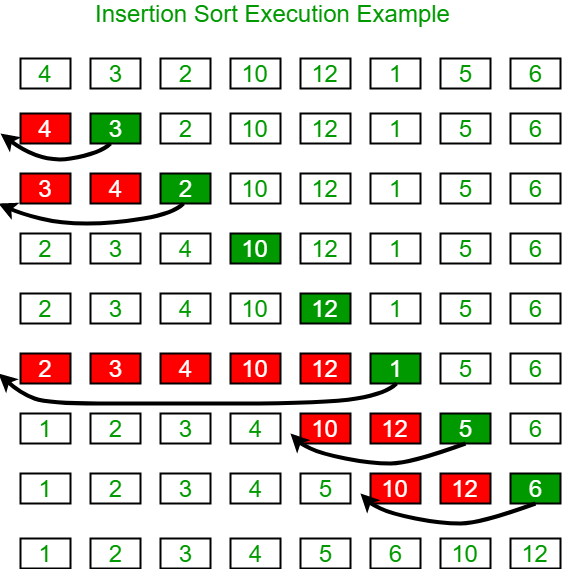
Searching & Sorting
Sorting Algorithms
First Pass:
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
Second Pass:
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
Third Pass:
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Selection Sort
The selection sort algorithm sorts an array by repeatedly finding the minimum element (considering ascending order) from unsorted part and putting it at the beginning. The algorithm maintains two subarrays in a given array.
Bubble Sort is the simplest sorting algorithm that works by repeatedly swapping the adjacent elements if they are in wrong order.
Example:
First Pass:
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
First Pass:
( 5 1 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 5 4 2 8 ), Here, algorithm compares the first two elements, and swaps since 5 > 1.
( 1 5 4 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 5 2 8 ), Swap since 5 > 4
( 1 4 5 2 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Swap since 5 > 2
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 ), Now, since these elements are already in order (8 > 5), algorithm does not swap them.
Second Pass:
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 4 2 5 8 )
( 1 4 2 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 ), Swap since 4 > 2
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
Now, the array is already sorted, but our algorithm does not know if it is completed. The algorithm needs one whole pass without any swap to know it is sorted.
Third Pass:
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
( 1 2 4 5 8 ) –> ( 1 2 4 5 8 )
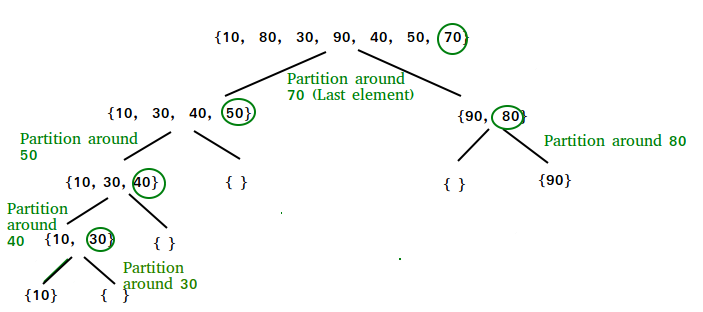
- Always pick first element as pivot.
- Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
- Pick a random element as pivot.
- Pick median as pivot.
The key process in quickSort is partition(). Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x. All this should be done in linear time.
Merge Sort
QuickSort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It picks an element as pivot and partitions the given array around the picked pivot. There are many different versions of quickSort that pick pivot in different ways.
- Always pick first element as pivot.
- Always pick last element as pivot (implemented below)
- Pick a random element as pivot.
- Pick median as pivot.
The key process in quickSort is partition(). Target of partitions is, given an array and an element x of array as pivot, put x at its correct position in sorted array and put all smaller elements (smaller than x) before x, and put all greater elements (greater than x) after x. All this should be done in linear time.

Merge Sort
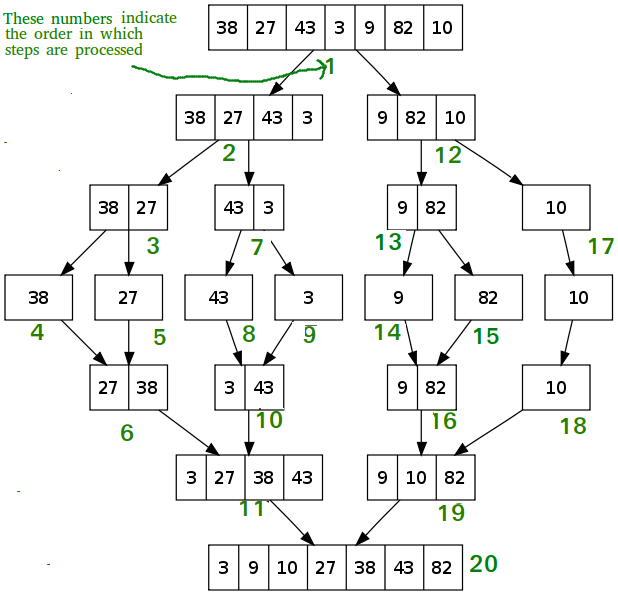
Merge Sort is a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It divides input array in two halves, calls itself for the two halves and then merges the two sorted halves. The merge() function is used for merging two halves. The merge(arr, l, m, r) is key process that assumes that arr[l..m] and arr[m+1..r] are sorted and merges the two sorted sub-arrays into one. See following C implementation for details.

Searching Algorithms
Searching Algorithms are designed to check for an element or retrieve an element from any data structure where it is stored. Based on the type of search operation, these algorithms are generally classified into two categories:
- Sequential Search: In this, the list or array is traversed sequentially and every element is checked. For example: Linear Search.
- Interval Search: These algorithms are specifically designed for searching in sorted data-structures. These type of searching algorithms are much more efficient than Linear Search as they repeatedly target the center of the search structure and divide the search space in half. For Example: Binary Search.
Linear Search
Linear search is a
very simple search algorithm. In this type of search, a sequential search is
made over all items one by one. Every item is checked and if a match is found
then that particular item is returned, otherwise the search continues till the
end of the data collection.
Binary Search
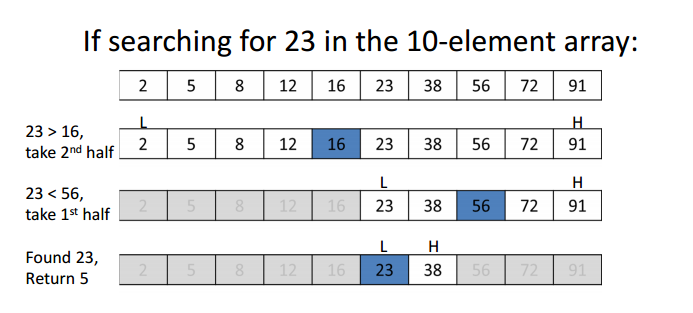
Search a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. Begin with an interval covering the whole array. If the value of the search key is less than the item in the middle of the interval, narrow the interval to the lower half. Otherwise narrow it to the upper half. Repeatedly check until the value is found or the interval is empty.
Interpolation Search
Interpolation search is an improved variant of binary search. This search algorithm works on the probing position of the required value. For this algorithm to work properly, the data collection should be in a sorted form and equally distributed.
Searching Algorithms are designed to check for an element or retrieve an element from any data structure where it is stored. Based on the type of search operation, these algorithms are generally classified into two categories:
- Sequential Search: In this, the list or array is traversed sequentially and every element is checked. For example: Linear Search.
- Interval Search: These algorithms are specifically designed for searching in sorted data-structures. These type of searching algorithms are much more efficient than Linear Search as they repeatedly target the center of the search structure and divide the search space in half. For Example: Binary Search.
Linear Search
Linear search is a
very simple search algorithm. In this type of search, a sequential search is
made over all items one by one. Every item is checked and if a match is found
then that particular item is returned, otherwise the search continues till the
end of the data collection.

Binary Search
Search a sorted array by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half. Begin with an interval covering the whole array. If the value of the search key is less than the item in the middle of the interval, narrow the interval to the lower half. Otherwise narrow it to the upper half. Repeatedly check until the value is found or the interval is empty.

Interpolation Search
Interpolation search is an improved variant of binary search. This search algorithm works on the probing position of the required value. For this algorithm to work properly, the data collection should be in a sorted form and equally distributed.